WHAT IS BLE?
Abbreviation of BLE derives as Bluetooth Low Energy. As the name says BLE works on very low power consumption when compared to classic Bluetooth.
Introduction and history
BLE is a subset of classic Bluetooth generally referred and introduced as Bluetooth smart by Bluetooth special interest group (SIG) in 2011 on Bluetooth version 4.0.
BLE was originally developed by Nokia as an in-house project called ‘Wibree’ and soon after was adopted by the Bluetooth SIG. As Bluetooth, BLE also uses a 2.4 GHz unlicensed radio band to interconnect nearby devices. It provides a data rate of up to 1 Mbps while consuming just 0.01 to 0.5 watts.
HOW BLE IS DIFFERENT?
BLE is developed on Bluetooth by adding or removing the layers of the protocol stack.
- Key difference can be noted between BLE and Bluetooth classic is low power consumption. BLE devices will work on battery for (4 to 5) years
- BLE is developed for IoT based products. Data communicated over BLE is generally a small packet in terms of size.
- BLE remains in sleep mode constantly except for when a connection is initiated. The actual connection times are only a few mS, unlike Bluetooth which would take ~100mS. The reason the connections are so short is that the data rates are so high at 1 Mb/s.
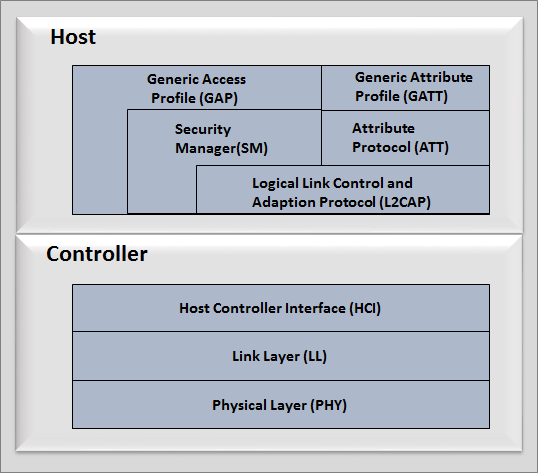
BLE STACK ARCHITECTURE
BLE stack contains host and controller. The controller is more determined as hardware. In the host side let’s see little about GAP and GATT, this is generally concentrated by application engineer.
Classic Bluetooth provides set of standard Bluetooth profiles, whereas BLE is specially designed to develop the required profiles for the application which consists of small data communication between the BLE devices. GATT layer on the stack is responsible for this data communication.
GAP (Generic Access Profile)
The GAP layer of the protocol stack is responsible for connection functionality. This layer handles the access modes and procedures of the device including,
- Device discovery
- Link establishment
- Link termination
- Initiation of security features
- Device configuration.
See the below pictorial representation of GAP State Diagram.

The application and profiles can directly call GAP API’s to perform functions like advertising or connecting. Most of the GAP functionality is handled by the GAPRole Task. GAP Abstraction shows this abstraction hierarchy.
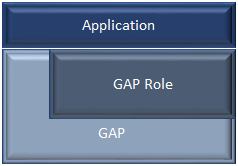
Use the GAPRole task rather than direct calls when possible. Configuring the GAP Layer describes the functions and parameters that are not handled or configured through the GAPRole task and must be modified directly through the GAP layer
GATT (Generic Attribute Profile)
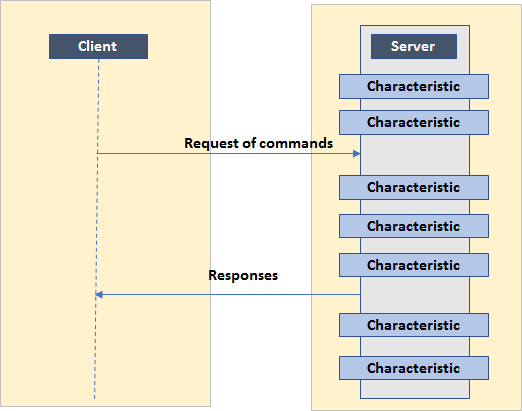
Just as the GAP layer handles most connection-related functionality, the GATT layer of the BLE protocol stack is used by the application for data communication between two connected BLE devices. Data is passed and stored in the form of characteristics in memory on the BLE device. From a GATT standpoint, when two devices are connected, they are each in one of two roles.
The GATT server
The device containing the characteristic database that is being read or written by a GATT client.
The GATT client
The device that is reading or writing data from or to the GATT server.
The GATT roles of client and server are independent from the GAP roles of peripheral and central. A peripheral can be either a GATT client or a GATT server, and a central can be either a GATT client or a GATT server. A peripheral can act as both a GATT client and a GATT server.
Like the GAP layer, the GATT layer is also abstracted. This abstraction depends on whether the device is acting as a GATT client or a GATT server. As defined by the Bluetooth Core Specification Version 5.0, the GATT layer is an abstraction of the ATT layer.
GATT Client Abstraction
GATT clients do not have attribute tables or profiles as they are gathering, not serving, information. Most of the interfacing with the GATT layer occurs directly from the application.

GATT Server Abstraction
As a GATT server, most of the GATT functionality is handled by the individual GATT profiles. These profiles use the GATT server application. Below figure shows GATT server abstraction.

The design process involves creating GATT profiles that configure the GATT server application module and use its API to interface with the GATT layer. In this case of a GATT server, direct calls to GATT layer functions are unnecessary. The application then interfaces with the profiles.
HOW BLE IS DIFFERENT FROM BLUETOOTH?
Below figure shows Bluetooth classic, Bluetooth smart ready and Bluetooth smart (BLE) stack structure. This figure shows how BLE is different from other two architecture.

- As previously mentioned, Bluetooth classic will provide set of standard services where as in BLE, profiles are developed, provided by the GATT – profile. In Bluetooth classic, SDP (service discovery protocol) which will discover the standard services available.
- Bluetooth smart ready is the combination of both Bluetooth smart ready and Bluetooth smart.
BLE IN PLACE OF BLUETOOTH! or BLE VS bLUETOOTH!
As described above, BLE is developed on top of Bluetooth for requirements like low power and small packet of data transaction. So, considering the application where its going to be used, one need to choose BLE or Bluetooth.
Everything is becoming smart day by day. Below are some of the major areas where BLE is contributing to become the world smart.
- Home automation
- Medical services
- Agriculture
- Beacons
- Automotive